When companies undergo the process of transformation as they seek to differentiate themselves and solve for ever-evolving consumer pain points, it’s not uncommon for new ideas, product lines or service spinoffs to hatch. Unrealized possibilities tend to be unearthed and opportunities to break into new audience segments are revealed.
Many organizations soon encounter the challenge of fitting new brand offerings within the original parent brand. With each addition to the product or service line, do you create a different name, package, and marketing strategy? What is the best way to maximize the value of both the unique offering and the brand as a whole when you introduce something new?
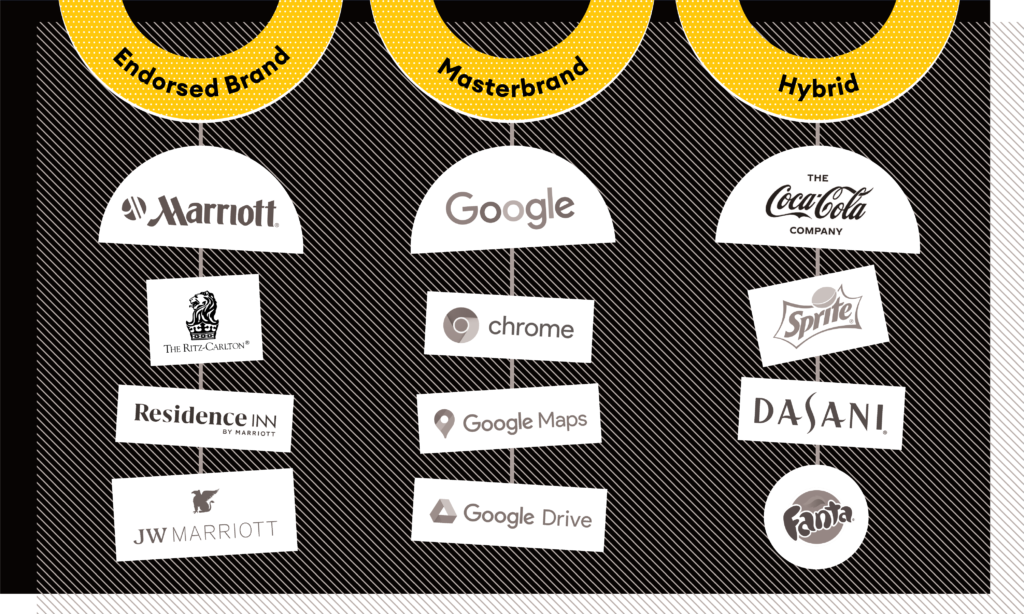
There are several common approaches: masterbrand, endorsed, individual, and hybrid. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages depending on your goals and the needs of your customer.
When to Link Brands Together
If your company makes multiple products or offers multiple services that play well together, you’ll most likely have success sub-branding them or creating a brand extension. This type of structure can include the following approaches:
- The endorsed brand in which each sub-brand may carry the same values, but will have its own distinct brand identity. An example would be Marriott with its JW Marriott, Residence Inn and Ritz Carlton sub-brands.
- The branded house or masterbrand in which the parent brand influences the identity of the sub-brand. An example here is Google with Chrome, Maps, Drive, etc.
- The hybrid, which is a blend of individual and masterbrand. Coca-Cola Company for example, has multiple individual product brands like Sprite, Dasani, Fanta, etc., but they also have their series of classic Coca-Cola products.
The so-called “halo effect” of sub-branding in the hybrid brand scenario can permeate into new audiences who may not be served directly by the parent brand’s core offering.
Let’s look at Uber Freight as an example.
Created by the parent company Uber, Uber Freight looks, feels and performs much the same as the app the company is best known for, but it serves a completely different, and very niche, audience. Based on the needs of this particular audience, the brand was able to take the “Uber experience” and tailor it to this untapped segment while maintaining its core brand principles. Uber didn’t stray from its core offering of better transportation, but the two brands have completely different strategies for attracting users and a different voice, tone and messaging.
Uber knew that when it came to truckers, they didn’t have the benefit of brand recognition – in fact, most truckers at that time had never even heard of the app. The company had to take a step back and really learn the market: The pain points, how to get truckers to adopt new technology, and how to communicate with them. The Uber Freight team hyper-focused on a specific region (in this case, Dallas), hired people who were experts in the industry and could speak the language, and began more of a direct outreach approach. A sub-brand with the same underlying purpose as the namesake brand, but a different approach and infrastructure for gaining users.
If your company offers multiple products or services that appeal to distinctly different audiences…
Then, in this case, the individual brand approach might be more fitting. Companies that offer multiple products or services that appeal to distinctly different audiences, so much so that a given customer likely wouldn’t even consider buying one product but would be very interested in another, could benefit from brand individuality.
This is not to be confused with brand extension, whereby a company will branch out into completely different product spaces altogether (like Guinness brewing beer and publishing a book of records). An individual brand is more like a sub-brand with a completely different look, feel and even price point. It’s where a parent brand will have a series of unrelated, independent brands under its umbrella. Think Unilever with Dove, Persil, Vaseline, Lipton, Korr, etc.
With the individual approach, each brand has vastly different personas they appeal to. Going the individual route is tricky for this precise reason, but the opportunity to increase personalization with each brand in order to reach disparate audiences can be enticing for organizations.
Also read: What Is CX & Why Does It Matter?

When To Build From Scratch
Finally, in some cases you’ll find two completely disparate brands that ultimately can be traced back to one company. This is often done if the two brands serve different audiences and have completely different visions and values. If the new product or service aims to fulfill different purposes and doesn’t share a particular stance, it may be best to completely separate the two brands.
If the new product or service aims to fulfill different purposes and doesn't share a particular stance, it may be best to completely separate the two brands.
When this occurs, the originating entity often doesn’t publicize the fact that they are behind the two brands, and in many cases customers of either brand is none the wiser the other exists. This tends to be the least common of the three brand architectures, as most organizations have an underlying vision, purpose or stance that is echoed throughout each of their offerings.
Also read: What’s In Store? The Future of Retail in a Post-COVID World
How to Know Which Strategy Is Best For You
The answer on which direction to go often lies within your vision, values and customers. Does your current customer base have a need that this particular product or service solves for? Does the new product fulfill upon your existing brand’s deeper purpose and vision, or does it have a completely different mission of its own? Answering these will help you determine which approach is the best option.
Keep in mind, if you commit to the individual branding approach, while it’s not completely necessary to make perfectly clear the brand connection, it is important to ensure you carry the same vision and values through each of your separate offerings.
The answer on which direction to go often lies within your vision, values and customers.
Another advantage of individual vs. pure sub-branding is that one misstep with a individual brand won’t damage your overall organization as much as a sub-branded failure. Because most sub-brands are visually and tonally in line with each other, bad publicity or a colossal failure in even a smaller venture can have disastrous consequences. We’ve seen this play out with well known brands like Samsung with its Galaxy Note 7 and Apple – even the most diehard Apple fans will abandon the brand across the board if one product doesn’t meet their expectations.
Individual brands don’t carry quite the same risk, though the lack of obvious association can be a drawback if a smaller off-shoot brand performs particularly well. It’s also worth noting, when a company brand spins off too many offshoot product brands all geared towards a similar audience segment, it can cause a tremendous amount of confusion.
An example of this is Centrieva, an accreditation management software for higher education. They launched a series of new products, each with its own brand name and all for a tangential market, and consequently, their customers and prospects became increasingly confused about the offerings. The solution to this problem was to parse out Centrieva as the corporate brand (which would live in the background) and create Weave as the master brand with each product as a sub-brand of Weave. In applying “Weave” to each product name, we helped create brand association and recognition and showed how each product works together as one cohesive platform.
On the path to transformation, as you uncover the latent (or obvious) wants, needs and desires of your audience, it will become more clear which brand architecture is best suited for your organization. You may discover, like Uber did, that you are dealing with a completely different audience segment who doesn’t even know you currently exist. If you’re creating a product that addresses a subsequent pain point of your existing audience, your brand name will likely carry levity. And in that case, you could go the route of Virgin, applying your brand name to product descriptions or sub-brands.
Note: This article was originally published on October 11, 2017 and updated and republished on December 29, 2020.



