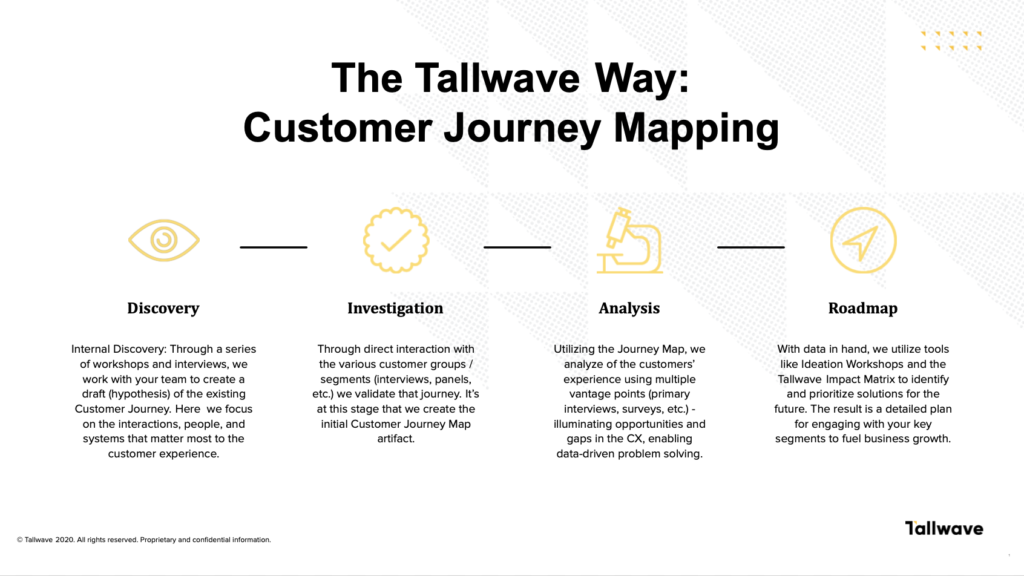
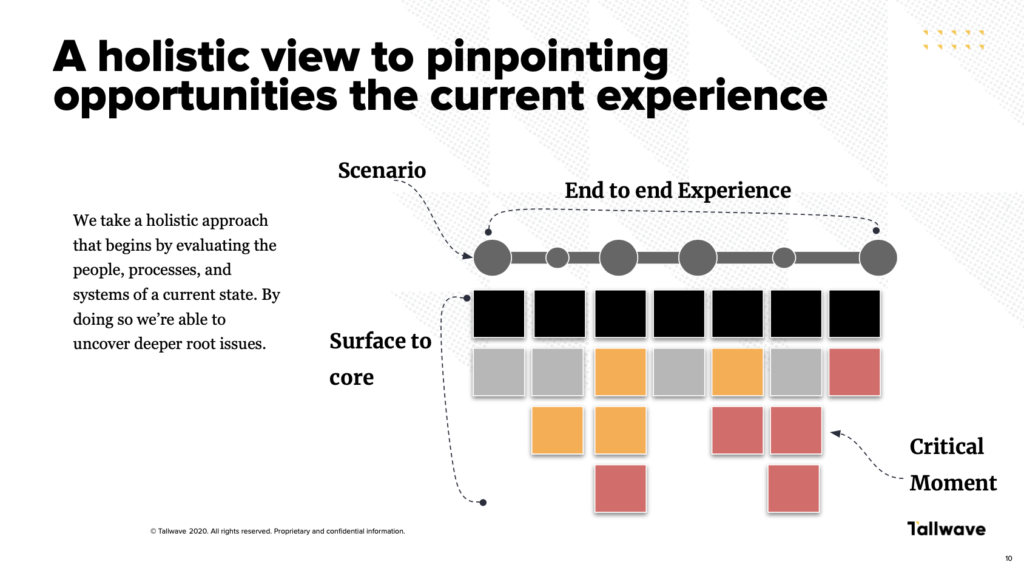
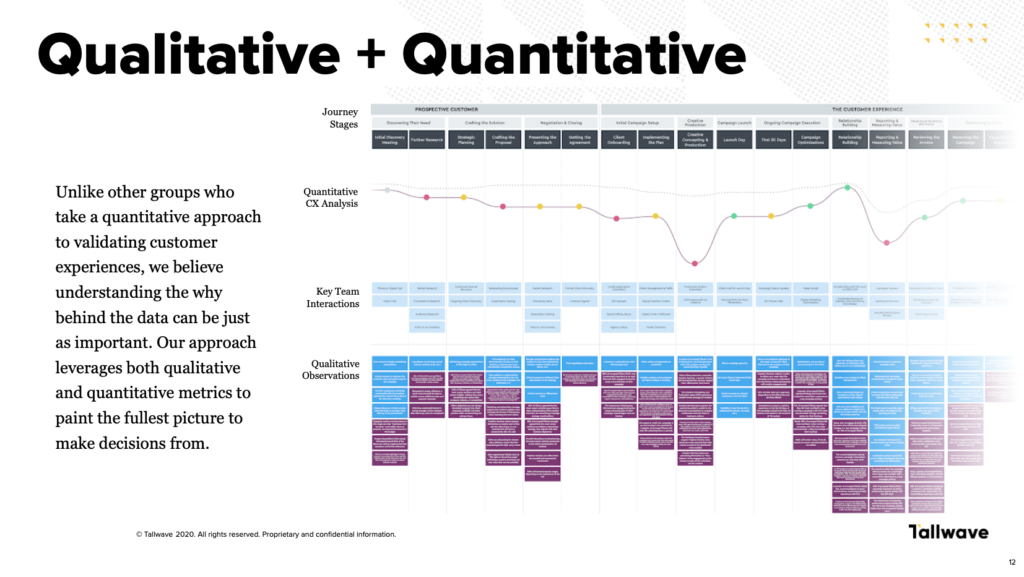
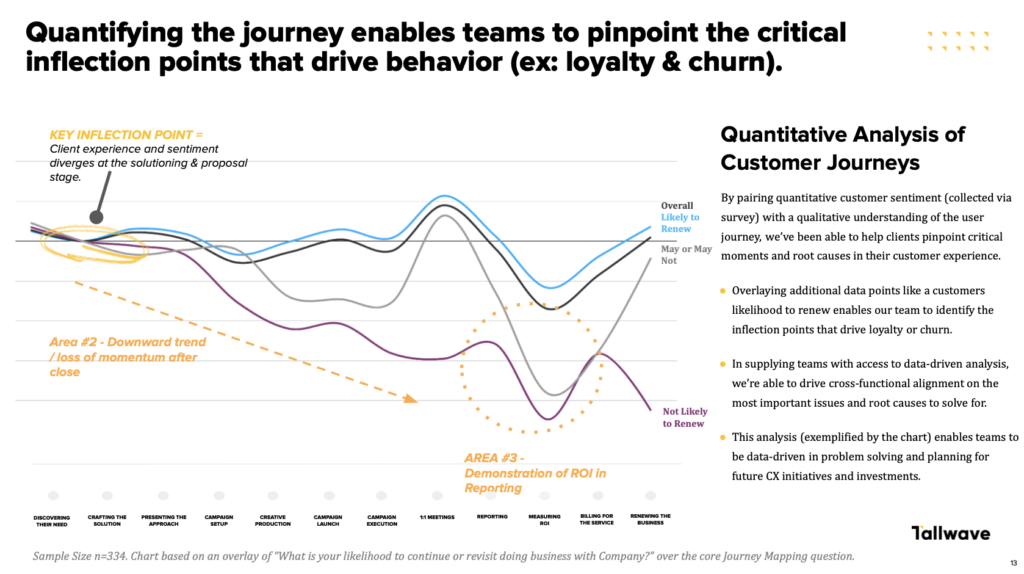
Gaining new customers is only half the battle when it comes to sustaining a healthy business — keeping customers engaged and loyal to your company long-term is just as important. Sometimes, that’s easier said than done, especially considering the changing nature of customer preferences.
Most companies are challenged with constantly iterating their customer engagement strategies. Oftentimes larger enterprise companies bear more of that brunt in order to maintain market share as more agile upstarts join the scene.
Also read: Data Driven Insights Into the Evolving Customer Experience
Case and point: A large entertainment and communications firm – despite having experience that predates the internet – came to us with plummeting retention rates. Identifying the cause of their customer churn was essential to strategizing and implementing an improved experience for the future. By conducting research to understand the end-to-end customer journey, we were able to uncover and map out internal and external stakeholder perspectives at each stage. Using that information, we identified which stages in the journey had the greatest impact on customer loyalty. Then we were able to create a prioritized list of suggested improvements to enhance the customer experience and drive a greater bond between the business and their audience.
It’s this kind of work that can make the world of difference when it comes to increasing customer engagement.
Reducing friction and inspiring trust are the cornerstones of customer engagement today. A recent Salesforce study found that 95% of consumers said trust makes them more likely to remain loyal while 80% said the customer experience is just as important as the product or service.
Reviewing the journeys your customers take helps to identify ways to increase convenience and drive engagement, which is essential for success. Here are some top methods to measure customer engagement.
Reducing friction and inspiring trust are the cornerstones of customer engagement today.
Top Customer Engagement Metrics
There are a variety of metrics you can use to create a full picture of your customer experience and increase customer engagement. Here are some of the most frequently used methods::
1. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS is the leading metric for measuring customer satisfaction and loyalty. This is accomplished by asking customers one, simple question to rate the likelihood that they would recommend a company, product or service to a friend or colleague. The rating is on a scale of 0 -10, with zero being “not at all likely” and 10 being “extremely likely.”
How to calculate: Respondents are divided into three groups based on their score.
- Promoters: (rated 9-10) are loyal customers who will also refer others to your company.
- Passives: (rated 7-8) are satisfied, but not enthusiastic.
- Detractors: (rated 0-6) are unhappy customers and could potentially damage your brand by spreading negative reviews.
To calculate your NPS score, subtract the percent of Detractors from the percent of Promoters. Here’s what the formula looks like: % Promoters – % Detractors = NPS. Your NPS can range anywhere from -100 to 100 depending on your ratio of promoters to detractors.
% Promoters - % Detractors = NPS
How it infers customer engagement: Your NPS score is a good measure of your customers’ overall perception of your brand. Customers who fit the Detractor category are unhappy, these are the customers most likely to speak poorly about your brand to others or leave negative reviews. Customers who fit the profile of Passives are not excited about your business and are unlikely to be loyal if a competitor comes along with a sweeter offer. Customers who are considered Promoters are not only loyal, but will act as ambassadors for your company. It’s best to compare your NPS to others in your industry and also to your past scores to monitor any changes in your customers’ perceptions.
Also read: The What, Why, & How Of Customer Behavior Analysis
Best for: This classic customer engagement tool is best for gaining a high-level understanding of customer experience and how loyal your customers are.
2. Customer Satisfaction (CSAT)
CSAT is short for Customer Satisfaction Score. It is a popular metric to gauge customer satisfaction levels for a specific product/service or action you took rather than an ongoing customer relationship.. A CSAT score is expressed as a percentage (100% to 0%). Using the results from a customer surveys that ask respondents to “Rate their overall satisfaction with the goods/services they received. Respondents use the following 1-5 scale:
1 = Very Dissatisfied (or Very Bad)
2 = Somewhat dissatisfied (Poor)
3 = Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied (Neutral)
4 = Somewhat satisfied (Good)
5 = Very Satisfied (Excellent)
How to calculate: To understand your CSAT, you’ll want to divide the number of satisfied customers (represented by those who responded with a 4 or 5 ) by the total number of customers.
Use this formula to calculate: Number of satisfied customers (4 and 5) / Number of survey responses) x 100 = % of satisfied customers
Number of satisfied customers (4 and 5) / Number of survey responses) x 100 = % of satisfied customers
How it infers customer engagement: Your CSAT score is helpful to measure customer satisfaction after an experience or touchpoint with your business. It’s not typically used to represent customer engagement over time, since it’s a snapshot of how each individual customer was feeling during the exact circumstances of the survey.
Best for: CSATs are typically easier to collect than other data points because you’re not asking a lot of your customers. CSATs are also easily understood across many channels of your organization. This makes them ideal for creating company-wide benchmarks that you can update consistently.
3. Customer Lifetime Value
Your customer lifetime value indicates how much your company can expect to earn across an entire relationship with a customer from start to finish. Segmenting your customers by lifetime value can help your company get strategic about the most important groups to engage for long term revenue growth.
How to calculate: Before you can calculate the customer lifetime value, you need to know the average customer value. You do this by determining the average purchase value and then multiplying that by the average number of purchases. That first formula looks like this: Average Purchase X Average Number of Purchase = Customer Value.
Average Purchase X Average Number of Purchase = Customer Value
Then, put that number into the following formula: Customer Lifetime Value = Customer Value X Average Customer Lifespan.
Customer Value X Average Customer Lifespan = Lifetime Value
How it infers customer engagement: It goes without saying that the happier your customers are with your product or service, the more likely they are to continue purchasing renewals or upgrades. Focusing on improving your customer lifetime value typically means you’ll surround customers with support and incentives, which can also lead to higher customer engagement scores. Best for: Compare your customer lifetime value to the cost of acquiring new customers so you can understand if your value realization is strong enough to offset the marketing or sales costs associated with generating demand.
4. User Activity
User activity measures how many unique customers are interacting with your product or service in a specific time frame — typically daily or monthly. This is an ideal customer engagement metric for SaaS companies or apps.
How to calculate: Calculating daily user activity hinges on accurately defining what you’ll consider a user and an activity. To get a strong sense of how users are interacting on your platform, you might want to count actions such as pulling reports or collaborating with team members instead of merely sign ons or app opens.
How it infers customer engagement: By measuring activities that would only happen if the user was engaged — like creating reports, for example — you can begin to understand how often your users are incorporating your features into their lives. If you notice some features are under-utilized, this could be a warning sign that your customers aren’t fully engaging with the potential of your offerings.
Best for: This metric is best for understanding what features of your product are most engaging for customers, so you can continue to iterate on these and improve your value realization opportunities.
5. Visit Frequency
Measuring the visit frequency shows you how often the same customer returns to your site or store location. This helps you to understand how familiar your customers are with your brand and the extent to which they are actively seeking your company.
How to calculate: Using Google Analytics, you can pull a count-of-session report to understand visit frequency to your website. Measuring visit frequency for brick-and-mortar locations has historically been more difficult, but new technology, such as Ripple Metrics, can actually measure return frequency in addition to other actions your customers take in store.
How it infers customer engagement: If you have many of the same customers returning over time, this shows a higher level of engagement. However, if you have customers visiting your site or location once and not returning, this shows you have more work to do in order to foster customer loyalty.
Best for: Visit frequency can be seasonal. For example, if you work at an oil change garage, you might only expect customers to return once every six months. That’s why measuring visit frequency is a good metric for companies that understand what the patterns of a happy customer look like. Gain clarity on the big picture of your customer journey so your visit frequency inferences will be valuable.
6. Screentime
Measuring how long a customer spends on your site can tell you how valuable your content is and the extent to which you are helping to make the lives of your customers easier. If your customers spend a long time reading an article or watching a video, congratulations, that means you gave them something to stick around for.
How to calculate: Using your website analysis tools, you can pull a report to specify the total time on site or get specific to understand how long customers are spending on each page.
How it infers customer engagement: If you notice customers are routinely spending a few seconds on each page, that could be a sign that your website content is not engaging. Typically the first action users take when they realize a webpage doesn’t have the information they need is to close it and move on to the next one. This metric can help you determine what content is hitting home with your customers and what needs more work.
Best for: This metric is essential if you rely on content marketing to drive sales or improve the customer experience.
Understanding your customer engagement isn’t always a matter of gathering the most information, but of understanding which metrics to focus on.
7. Pages per Session
Pages per session shows you the average number of pages a visitor to your website reads before they leave your website. Similar to screentime, this metric can show you the extent to which visitors are enjoying your website and gaining value from it.
How to calculate: You can determine the pages per session by dividing the total page views by the total amount of sessions for any given time period. If you use Google Analytics, this number should automatically be pulled for you through the program’s standard reporting in the acquisition overview section. To get more detailed, remember to segment by source. You might find that visitors coming from one channel are more heavily engaged, which could influence how you spend advertising dollars.
How it infers customer engagement: If you have a high number of pages per session it’s likely visitors to your site are finding a lot of useful information and that you are providing a quality user experience. If you find this metric drops over time, it could signal that you need to revisit your content or maintain your website.
Best for: Use this metric to understand how well your website is performing when it comes to serving your customers.
8. Churn Rate
Your churn rate measures the number of customers who are concluding their relationship with your business over a set period of time. For example, if you are a service with subscribers your monthly churn rate would show the percentage of users who have cancelled their subscription each month.
How to calculate: Calculating your churn rate is simple, just divide the number of customers who have stopped doing business with you by the total number of customers. For example, if you have 20,000 subscribers and 1,000 cancelled last month, you would have a churn rate of 5% for the month.
How it infers customer engagement: If you have a high churn rate you can infer that somewhere along the line your customers are becoming disappointed. You’ll need to do some work to understand where in the journey they are seeing less value so you can improve these pain points and extend the customer lifespan.
Best for: This is a good metric for softwares or subscription services that rely on monthly recurring revenue.
9. Social Media Engagement
Your social media engagement can show you how interested your customers are in hearing from you and sharing about the work you do. A high social media engagement rate doesn’t always equate to increased sales, but it can definitely help guide your team to know if you’re on the right track in developing rapport, loyalty and strong word-of-mouth.
How to calculate: To get a high-level view of your social media engagement, measure your average engagement rate by adding the total number of engagements on a given post (this includes likes, comments and shares) by your total number of followers.
How it infers customer engagement: If your social media engagement numbers are low, this could be a sign that you need to do more work providing daily value to your current customers to turn them into brand evangelists. Not all companies rely on social media though, so if your social engagement numbers are low but you have another channel that does well, such as a newsletter, you might want to weigh both sets of metrics against each other before taking action.
Best for: Social media engagement can help companies understand how well they are doing when it comes to creating brand awareness and enthusiasm.
Bottom Line
Understanding your customer engagement isn’t always a matter of gathering the most information, but of understanding which metrics to focus on. Every brand should choose a handful of metrics that matter most to their business operations. Depending on your goals, there are only a few metrics that should be tracked regularly to gauge engagement, loyalty, value realization and growth. For the client we mentioned at the start of this article, we were trying to solve for high customer churn. We decided to narrow available data down so we were only focusing on mapping customer satisfaction. We felt this metric could most accurately predict churn. By understanding where in the journey customers were least satisfied, we were able to identify where drop off occurred.